TCSPC
PUMP-PROBE
TCSPC-CSM
Observing
the local environment
Observing energy
transfer using
Observing
molecular scale organization
of a
molecular probe
pump-probe
spectroscopy
and interactions
[Learn
more]
[Learn
more]
[Learn more]
FRAP
LANGMUIR-BLODGETT TROUGH
Observing translation
diffusion
and
Forming monomolecular films and
monitoring
mobility of probe
molecules and
films
film formation and deposition
[Learn more]
[Learn
more]
|
TIME-CORRELATED
SINGLE PHOTON COUNTING
CONFOCAL SCANNING MICROSCOPE INSTRUMENT
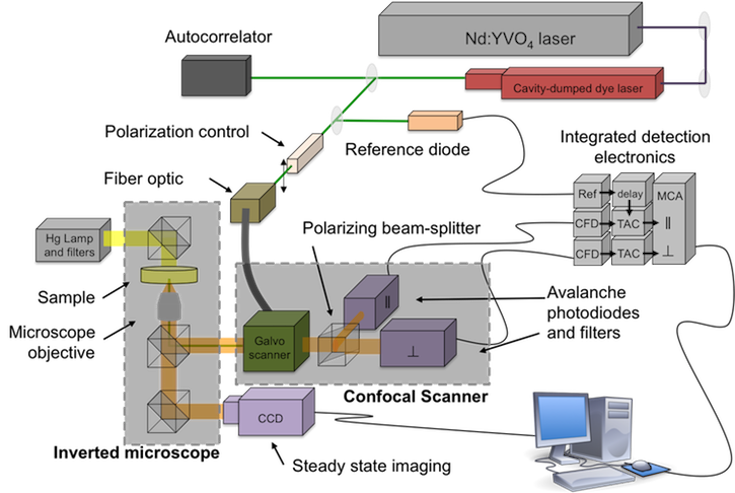
|
Schematic
of the time-correlated single photon counting confocal
scanning microscopy (TCSPC-CSM) instrument, showing source
beam (green), components of the inverted microscope, and
confocal scanner components.
|
FLUORESCENCE
LIFETIME AND ANISOTROPY IMAGING
MEASUREMENTS
The
time-correlated single photon counting confocal scanning
microscope (TCSPC-CSM) instrument is based on an inverted
microscope optical configuration. The microscope is
equipped with a mercury lamp illuminator for the
acquisition of steady state fluorescence images and with
10x-100x objectives. Detection of time-resolved data is
achieved with a polarized dual channel confocal scanning
instrument attached to an output port of the microscope
and controlled by a galvo-drive unit.
The confocal scanner is equipped with a polarizing beam
splitter and two avalanche photodiode detectors for the
acquisition of fluorescence lifetime and anisotropy decay
images. Polarized fluorescence transients used in the
generation of images are acquired using time-correlated
single photon counting detection electronics.
The light source for this instrument is a synchronously
pumped cavity dumped dye laser excited by the output of a
passively mode locked Nd:YVO4 laser. The source laser
produces 13 ps pulses at 80 MHz repetition rate. The dye
laser is cavity dumped to control the repetition rate. The
dye laser output can be tuned from 430 to 850 nm depending
on the dye and optics used and the excitation wavelength.
Steady state fluorescence images are acquired using an
illuminator and a CCD camera, both mounted on the inverted
microscope.
|
|
|
|

