
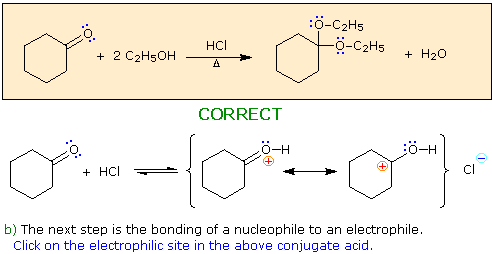
a) The first step in this process must be an acid-base proton transfer.
Click on the basic atom that is protonated to initiate this transformation.
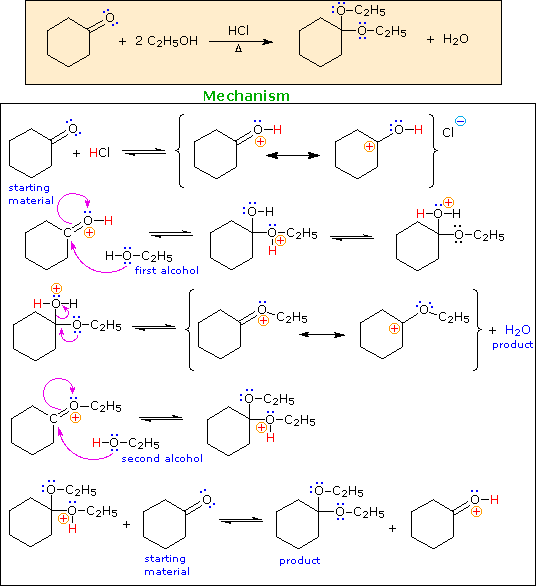
Acetal derivatives of aldehydes and ketones are prepared by an acid-catalyzed dehydration reaction with alcohols or diols. An example is shown below.
Writing a mechanism for this reaction provides a good test of ones' understanding of acid-catalyzed processes.

a) The first step in this process must be an acid-base proton transfer.
Click on the basic atom that is protonated to initiate this transformation.
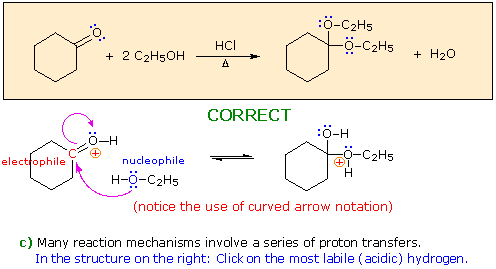
When you have made a correct selection, an equation showing the reaction for that step will appear, and a new question will be posed. Incorrect selections will open an alert window displaying an explanatory message. The overall transformation will remain displayed in the colored box at each stage.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
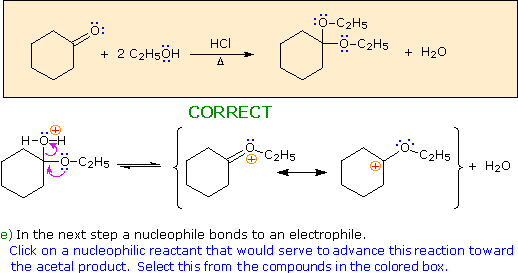
Choose a nucleophile from the reactants in the colored box.
![]()
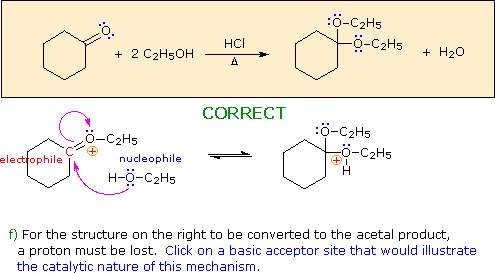
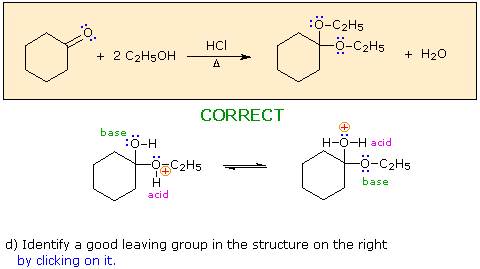
Hint: Choose a base from the reactants in the colored box.
![]()
![]()